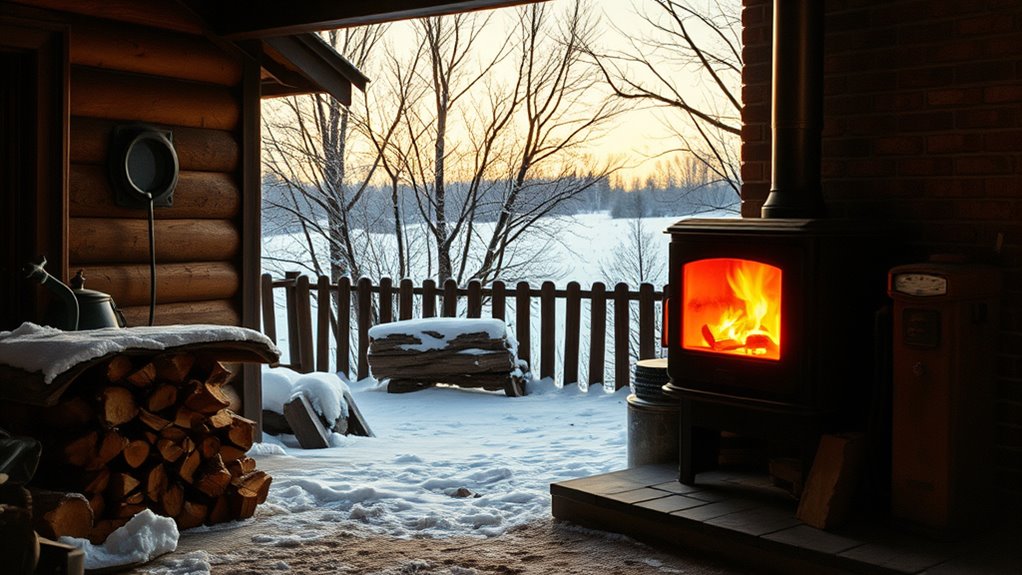
During the 1970s energy crisis, fuel shortages and rising costs pushed many households to rely on wood heating as a dependable, local energy source. As dependence on fossil fuels became problematic, families turned to wood due to its availability and improved stove technology. This surge in wood heat highlighted the importance of renewable energy and energy independence. To discover more about how this shift shaped energy solutions, keep exploring this important historical moment.
Key Takeaways
- The 1970s energy crisis caused fuel shortages, prompting households to turn to wood heating as a reliable alternative.
- Rising energy prices and supply disruptions increased interest in renewable energy sources like wood heat.
- Technological improvements in wood stoves made burning wood safer, more efficient, and more attractive.
- The crisis highlighted the importance of energy independence and local sourcing of heating fuel.
- The resurgence of wood heat during this period demonstrated resilience and adaptability in energy consumption.
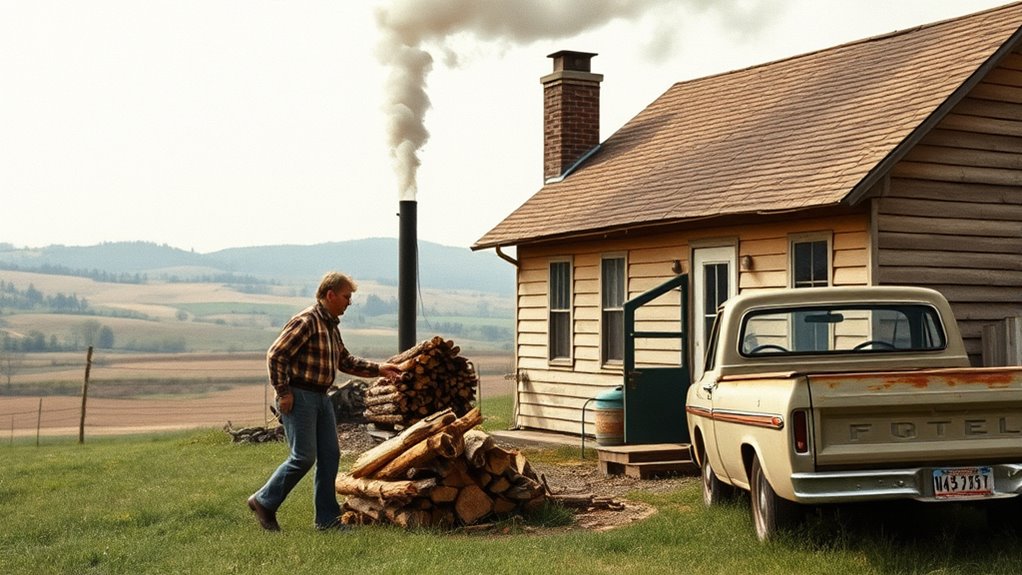

As the global energy crisis worsens, more households are turning back to wood heat as a reliable and affordable alternative. During the 1970s, fuel shortages and rising energy prices pushed many to reconsider traditional heating methods. At that time, the reliance on fossil fuels like oil and natural gas became increasingly problematic, especially as geopolitical tensions disrupted supply chains. This period highlighted the importance of renewable energy sources, and wood heat emerged as a practical solution. Unlike finite fossil fuels, wood is renewable, provided you harvest responsibly, making it an appealing option for those seeking energy independence. You might find that using wood for heating not only reduces your dependence on volatile fuel markets but also offers a sustainable way to stay warm during uncertain times.
During the 1970s energy crisis, fuel shortages became a stark reality for many households. Gasoline rationing, oil embargoes, and shortages of heating fuels left people scrambling for alternatives. As supplies dwindled, households that previously relied solely on conventional fuels had to adapt quickly. Wood, which had been a traditional heating source for centuries, experienced a resurgence as families looked for ways to maintain warmth without relying on increasingly scarce and expensive fuels. This shift was driven by the recognition that wood could be stored easily, transported locally, and used efficiently in wood stoves and fireplaces. Many homeowners invested in better heating appliances, which improved the efficiency of wood burning and made it a more viable option during this period of fuel shortages.
The 1970s also sparked a broader interest in renewable energy, as people began to understand that fossil fuels were not only finite but also environmentally damaging. The energy crisis underscored the importance of diversifying energy sources, and wood heat fit into this vision perfectly. It provided a form of energy that could be locally sourced and managed, reducing dependency on imported fuels. This mindset encouraged innovations in wood stove technology, making it safer and more efficient, and it laid the groundwork for future renewable energy initiatives. For you today, understanding this history emphasizes the value of renewable energy options like wood heat, especially as fuel shortages continue to threaten energy security worldwide. The resurgence in wood heating during the 1970s demonstrates how crises can drive innovation and adaptation, lessons that remain relevant in today’s energy landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Did the 1970S Energy Policies Influence Renewable Energy Adoption?
You see that during the 1970s, policy shifts aimed at achieving energy independence, which encouraged renewable energy adoption. Governments introduced incentives and regulations to promote alternative energy sources, including wind, solar, and biomass. These policies made renewables more attractive and accessible, laying the groundwork for ongoing development. As a result, you benefit from increased renewable options, reduced reliance on fossil fuels, and a more sustainable energy future driven by those early policy changes.
What Technological Innovations Supported Wood Heating During the Resurgence?
You see, innovative combustion technologies and pellet stoves revolutionized wood heating during the resurgence. These advancements made burning wood more efficient and eco-friendly, reducing emissions and increasing heat output. The pellet stove, in particular, offered a clean, automated alternative to traditional fires, making wood heating more appealing and accessible. This technological leap transformed wood heat from a rustic option into an efficient, modern energy source.
Were There Environmental Concerns Linked to Increased Wood Heating Use?
You might be concerned about environmental issues from increased wood heating. Yes, indoor air quality can suffer due to smoke and particulates, affecting respiratory health. Additionally, if not managed properly, wood harvesting could threaten forest conservation by leading to deforestation or habitat loss. It’s important to balance wood heat use with sustainable practices to protect both air quality indoors and forest ecosystems outside.
How Did Government Incentives Impact Wood Heat Adoption?
Government grants and tax incentives considerably boosted your adoption of wood heating. These incentives made it more affordable for you to invest in wood stoves and related equipment, reducing upfront costs. As a result, you were encouraged to switch to wood heat, benefiting from financial support that made sustainable options more accessible. This government assistance played a key role in increasing the popularity of wood heating during that period.
What Were the Socioeconomic Effects of the Energy Crisis on Rural Communities?
You might think rural communities suffered during the energy crisis, but many actually experienced increased resilience. As fossil fuel prices soared, rural areas boosted local employment through wood heating and energy production. This shift strengthened community bonds and created new economic opportunities. While challenges existed, the crisis pushed rural communities to become more self-reliant, fostering a sense of resilience that helped them adapt and thrive despite broader national hardships.
Conclusion
As you watch the flickering glow of a wood fire, you can feel the warmth spreading through your home, echoing a time when wood heat offered a simple, resilient solution during the energy crisis. The crackling logs remind you of a bygone era, rekindling a connection to nature and self-reliance. In those flames, there’s a quiet power—an enduring reminder that sometimes, going back to basics can light the way forward.